Concrete is one of the most widely used construction materials due to its versatility, strength, and durability. The quality of concrete, especially in its fresh state, directly affects the performance of the final structure. One of the most common and practical tests to evaluate the workability and consistency of fresh concrete is the concrete slump test. Understanding what is concrete slump test is essential for engineers, contractors, and site workers to ensure that concrete can be easily placed, compacted, and finished without compromising its strength. This test is simple, cost-effective, and widely recognized across construction standards worldwide, providing immediate feedback on the condition of concrete before it is poured.
Importance of What is Concrete Slump Test
The concrete slump test is important because it measures the workability of fresh concrete, which is critical for construction efficiency and structural integrity. Workable concrete ensures that the material can flow easily into formwork, surround reinforcement, and be compacted adequately to prevent voids or honeycombing. If concrete is too stiff, placement becomes difficult, leading to weak areas and poor bonding. If it is too fluid, segregation may occur, reducing strength and durability. By understanding what is concrete slump test, construction professionals can detect inconsistencies in the mix, adjust water content, and confirm that the concrete meets the design specifications for each project.
Principle Behind What is Concrete Slump Test
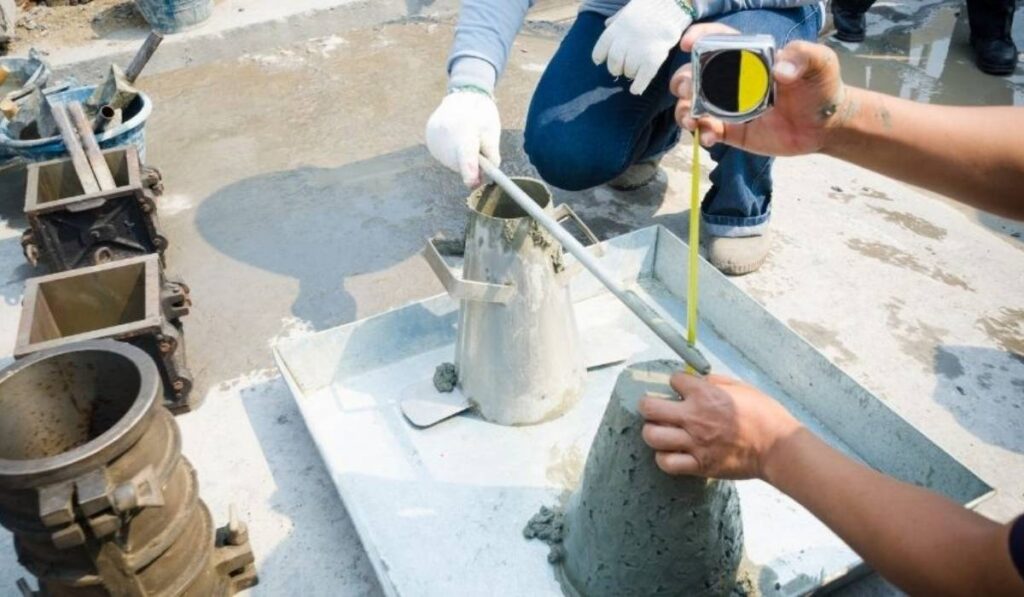

The principle of the concrete slump test is straightforward: it measures the vertical subsidence of freshly mixed concrete when removed from a conical mold. The slump indicates the concrete’s workability and flow characteristics. A standardized cone, filled in layers with tamping in between, is lifted vertically, allowing the concrete to settle. The difference in height between the mold and the settled concrete is recorded as the slump. This measurement reflects whether the concrete is stiff, plastic, or fluid, providing quick and reliable insight into the mix. Understanding what is concrete slump test helps site personnel interpret these readings and determine the suitability of the mix for placement.
Equipment Required for What is Concrete Slump Test
To perform what is concrete slump test correctly, several pieces of equipment are required. The standard tools include a metallic or plastic slump cone, a flat and rigid base plate, a tamping rod, and a measuring scale. Additionally, water may be needed to clean the equipment between tests. The simplicity of the equipment makes the test portable and convenient for field use. By using the proper tools, engineers can perform what is concrete slump test repeatedly on-site, ensuring that every batch of concrete is consistent and meets quality requirements.
Step-by-Step Procedure of What is Concrete Slump Test

Performing what is concrete slump test involves a standardized procedure to maintain accuracy. First, the slump cone is placed on a firm, level base. The cone is filled in three equal layers, each layer tamped thirty times with the rod to compact the concrete. After filling, the top surface is leveled, and the cone is carefully lifted vertically. The resulting vertical settlement of the concrete is measured from the original top of the cone to the highest point of the concrete after it settles. Recording the slump value accurately allows engineers to evaluate workability and determine if the mix requires adjustment before placement.
Types of Slump in What is Concrete Slump Test
During what is concrete slump test, three types of slump are commonly observed: true slump, shear slump, and collapse slump. True slump occurs when the concrete subsides uniformly, indicating a well-mixed and workable batch. Shear slump happens when one part of the concrete slides or shears off, suggesting poor cohesion or excessive water. Collapse slump occurs when the concrete collapses entirely, indicating an overly wet or unstable mix. Recognizing these types is critical for interpreting results and making adjustments. Understanding these variations is fundamental to understanding what is concrete slump test and its implications on construction quality.
Factors Affecting What is Concrete Slump Test

Several factors influence the results of what is concrete slump test. Water content is the primary factor; higher water-cement ratios result in higher slumps, while lower ratios produce stiffer mixes. Aggregate type, size, and grading also affect workability. Angular or poorly graded aggregates reduce slump, while smooth and well-graded aggregates improve it. Admixtures such as superplasticizers can enhance workability without increasing water content. Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity also play a role. Recognizing these factors allows engineers to interpret what is concrete slump test results accurately and make necessary adjustments.
Limitations of What is Concrete Slump Test
While what is concrete slump test is a valuable tool for assessing workability, it has limitations. It does not directly measure concrete strength, durability, or setting time. Very stiff or highly fluid mixes may yield inconsistent results, making the test less reliable for extreme conditions. Variations in technique, such as improper tamping or uneven lifting of the cone, can also affect accuracy. Despite these limitations, what is concrete slump test remains an essential field test due to its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ability to provide immediate feedback on concrete consistency.
Applications of What is Concrete Slump Test
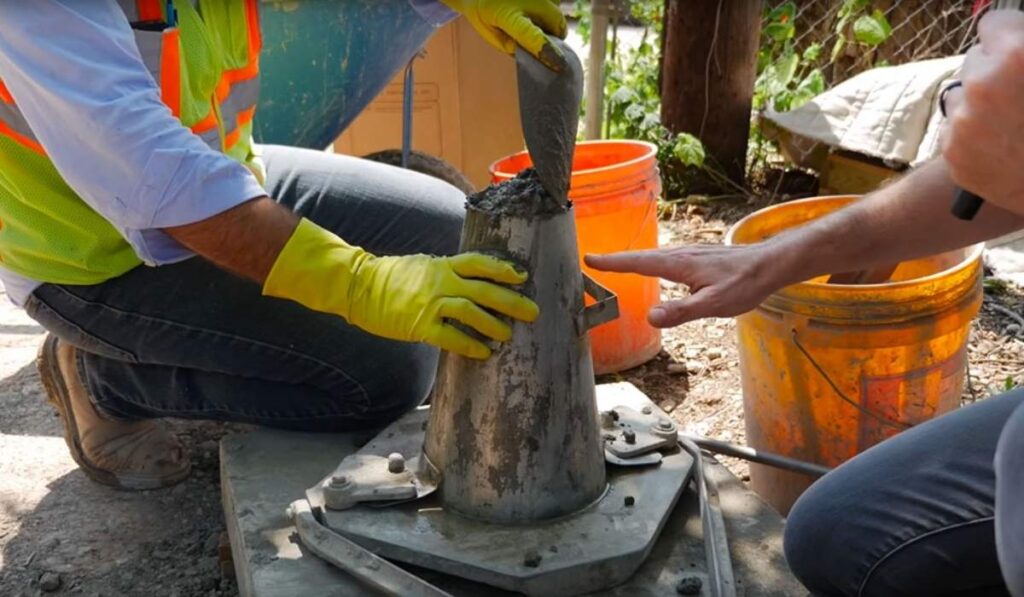

The concrete slump test has broad applications in construction. It is used to assess the workability of concrete for foundations, slabs, beams, columns, and pavements. Slump values help verify that the concrete mix delivered to the site matches design specifications and ensures proper placement and compaction. Additionally, it assists in adjusting water content or admixtures to accommodate environmental conditions or changes in materials. Understanding what is concrete slump test enables engineers to maintain quality control across different batches and construction phases, ensuring uniform performance and durability.
Best Practices for What is Concrete Slump Test
To achieve reliable results in what is concrete slump test, several best practices should be followed. Use standard equipment, perform the test on a firm, level base, and follow the procedure consistently. Tamping should be uniform for each layer, and measurements should be recorded immediately after the test. Repeating the test on multiple samples helps confirm consistency and detect any deviations in the mix. Clean equipment between tests to avoid contamination. Adhering to these practices ensures that what is concrete slump test provides accurate and actionable information for construction quality control.
Conclusion
Understanding what is concrete slump test is essential for anyone involved in concrete construction. This simple, reliable, and widely accepted method provides insight into workability, consistency, and quality of fresh concrete. By performing the slump test correctly and interpreting the results, engineers can ensure that concrete can be placed and compacted effectively, maintaining the strength and durability of structures. Despite its limitations, the concrete slump test remains a fundamental tool in construction quality control, helping professionals maintain high standards and achieve successful project outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is concrete slump test?
- A test to measure the workability and consistency of fresh concrete using a slump cone.
2. Why is concrete slump test important?
- It ensures concrete is workable, can be placed easily, and prevents voids or segregation.
3. What types of slump are observed?
- True slump, shear slump, and collapse slump indicate different mix properties.
4. What factors affect concrete slump test?
- Water content, aggregate type, grading, admixtures, and environmental conditions.
5. Can slump test determine concrete strength?
- No, it only measures workability, not strength or durability.