Musté is a fermented ingredient that has gained recognition for its versatility in both culinary and beverage applications. Its unique flavor, derived from a natural fermentation process, offers a combination of tanginess, subtle sweetness, and aromatic complexity. The use of musté spans traditional cuisines, modern gastronomy, and innovative beverages. Its ability to enhance taste, aroma, and texture makes it a staple for chefs, home cooks, and beverage artisans alike. Understanding musté requires exploring its fermentation process, historical context, nutritional benefits, and practical applications.
The Composition and Fermentation Process of Musté
At the core of musté is a natural fermentation process, where sugars are converted by yeast and bacteria into alcohol, organic acids, and aromatic compounds. This process not only preserves the ingredient but also enriches its flavor and health benefits. Musté typically contains water, fermentable sugars, and beneficial microorganisms that interact to produce a complex taste profile. Depending on the fermentation duration, temperature, and microbial composition, musté can vary in sweetness, acidity, and aroma. This adaptability is part of what makes musté a versatile ingredient in both cooking and beverage preparation.
Historical Background and Cultural Relevance
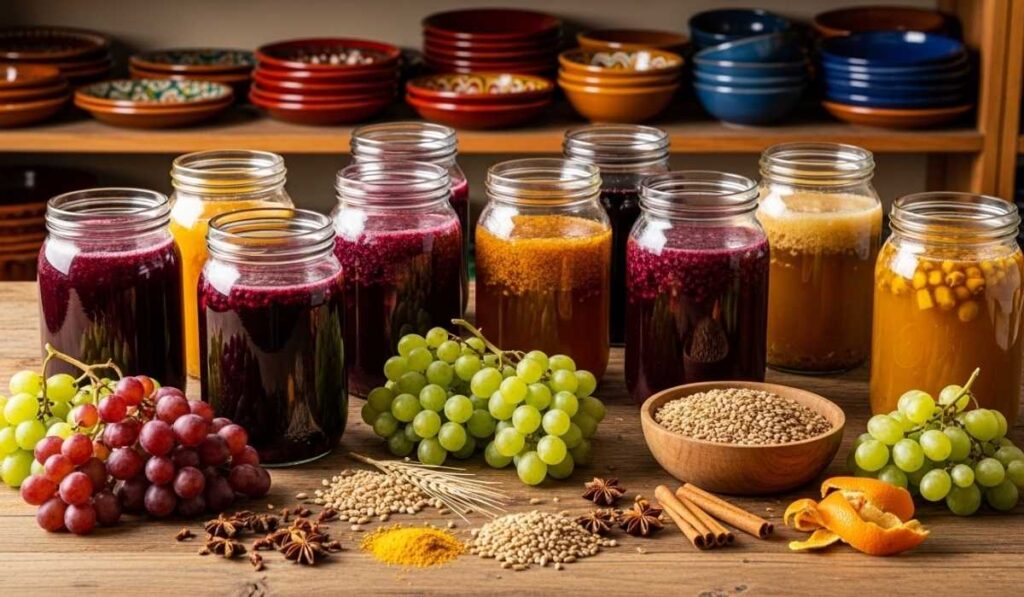

Historically, musté has been an essential component in traditional cuisines and ceremonial beverages. Many cultures have relied on musté for its preservative qualities and flavor enhancement. Ancient fermentation techniques allowed communities to produce beverages and sauces that could last longer while offering unique taste experiences. The cultural importance of musté is also reflected in its ceremonial uses, where it was considered both nourishing and symbolic. Its longstanding presence in culinary traditions demonstrates its value and enduring appeal.
Nutritional Benefits of Musté
Beyond flavor, musté provides nutritional benefits due to the fermentation process. Fermentation increases the bioavailability of nutrients, enhances digestibility, and introduces beneficial probiotics. Regular consumption of musté can support gut health, improve metabolism, and contribute to overall wellness. The ingredient also contains trace vitamins and minerals, which may vary depending on the source material used for fermentation. By incorporating musté into both food and beverages, consumers gain not only taste enhancement but also functional nutritional support.
Musté in Culinary Applications

In cooking, musté is prized for its ability to enhance flavor and complexity. Chefs use musté in sauces, dressings, marinades, and glazes to introduce acidity, sweetness, and umami. It can be reduced to intensify its flavor or blended with other ingredients for balance. Its versatility allows it to complement proteins, vegetables, grains, and baked goods. The culinary applications of musté demonstrate its capacity to transform ordinary dishes into rich and layered experiences.
Musté as a Beverage Base
As a beverage base, musté offers unique opportunities for both traditional and modern drinks. Fermented drinks made from musté can range from mildly effervescent refreshments to complex alcoholic beverages. Its natural sweetness and acidity provide a balanced flavor profile that pairs well with herbs, fruits, and spices. Mixologists and beverage producers increasingly incorporate musté to create signature drinks that highlight both its taste and health benefits. Its role in beverages underscores the versatility of musté as a multifunctional ingredient.
Production Techniques and Modern Innovations

Modern production of musté blends traditional fermentation knowledge with technological advancements. Controlled fermentation environments ensure consistency in flavor, safety, and quality. Innovations include precise temperature control, selective microbial cultures, and standardized fermentation periods. These advancements allow producers to create musté products that maintain traditional flavors while meeting contemporary culinary and beverage standards. The combination of heritage and innovation ensures that musté remains relevant in today’s food and drink industry.
Storage and Shelf Life
Proper storage of musté is crucial to maintaining its flavor and quality. Due to its fermented nature, musté should be stored in cool, dark conditions to prevent spoilage and over-fermentation. Bottled or sealed musté products often benefit from refrigeration, especially when used as beverage bases. Shelf life may vary depending on fermentation strength and the type of container used. Understanding storage requirements allows chefs, beverage artisans, and home users to maximize the usability and longevity of musté.
Challenges and Considerations

While musté is versatile, its preparation and use require care. Over-fermentation can lead to overly acidic or alcoholic flavors, while under-fermentation may result in a lack of depth. Understanding the balance of microbial cultures, sugar content, and fermentation duration is key to achieving consistent results. Additionally, incorporating musté into recipes may require adjustments in seasoning, cooking time, or complementary ingredients. Awareness of these challenges ensures successful use of musté in both culinary and beverage applications.
Future Prospects and Global Adoption
The future of musté looks promising as chefs, beverage producers, and health-conscious consumers increasingly seek functional and flavorful ingredients. With its combination of taste, nutritional benefits, and versatility, musté is poised to gain wider global recognition. Innovative recipes, health-focused beverages, and fusion cuisines are likely to integrate musté, promoting both cultural appreciation and modern culinary innovation. The growing interest in fermented foods and drinks ensures that musté will remain a valuable ingredient for years to come.
Final Thoughts on Musté
Musté stands as a remarkable example of how fermentation can create ingredients that are both functional and flavorful. Its ability to enhance dishes, serve as a beverage base, and provide nutritional benefits makes it an essential element in modern culinary practices. By combining traditional knowledge with contemporary production methods, musté continues to bridge heritage and innovation. For further information on fermented foods and beverages, you can explore musté within the broader context of fermentation and culinary traditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is musté?
- Musté is a fermented ingredient used as a culinary enhancer and beverage base.
2. How is musté made?
- Musté is created through natural fermentation of sugars by yeast and bacteria.
3. Can musté be used in cooking?
- Yes, musté enhances sauces, marinades, glazes, and baked goods with flavor.
4. Is musté healthy to consume?
- Yes, musté contains probiotics, nutrients, and aids digestion.
5. How should musté be stored?
- Musté should be kept in a cool, dark environment or refrigerated to maintain quality.